Voice Search Optimization Guide 2026: Boost Your Rankings
Table of Contents
Book a Free Demo Class

Voice Search Optimization Guide 2026: Boost Your Rankings
Voice search optimization in 2026 is no longer optional; it is part of how users naturally search on mobiles, smart speakers, cars, and AI assistants. When your pages are not optimized for conversational queries and quick voice answers, you miss high‑intent traffic that often converts better than generic keyword visits.
In 2026, assistants like Google Assistant, Siri and Alexa will increasingly pick one “best” answer instead of showing a long list of links. That means the websites which structure their content clearly, answer questions directly and load fast can capture a disproportionate share of traffic and leads.
For local and service‑based businesses, this is even more critical because many voice queries include strong intent phrases like “near me”, “open now” or “best [service] in [city]”.
Recent updates and unannounced tweaks have made search results more volatile in 2026, but the pattern is clear: Google wants fast, accurate, spam‑free answers that genuinely help users, not keyword‑stuffed pages written only for bots.
If you align with that direction using clean structure, strong EEAT, and natural language, your voice search rankings become more stable and your overall organic traffic improves.
Also read: Enroll in the Best SEO Course in Bareilly Today!
The Current Voice Search Landscape
| Platform | Market Share | Key Features |
|---|---|---|
| Google Assistant | 36% | Integration with Android devices, smart displays |
| Amazon Alexa | 25% | Smart home dominance, shopping capabilities |
| Apple Siri | 22% | iOS integration, privacy-focused |
| Other Assistants | 17% | Microsoft Cortana, Samsung Bixby |
The number of voice assistant users in the U.S. is expected to reach 162.7 million, with 93% of consumers satisfied with their voice assistants. This satisfaction rate indicates strong user adoption and the need for businesses to adapt their SEO strategies accordingly.
In this guide, we’ll cover everything you need to know about voice search optimization in 2026, including actionable strategies, technical SEO tips, content approaches, and analytics tracking.
Also read: SEO, AIO, GEO, AEO, SXO: What’s the Real Difference?
What is Voice Search Optimization?

Voice search optimization means getting your website ready to answer spoken questions from users on phones, smart speakers, and AI assistants.
When someone says “Hey Google, what is voice search optimization?” the assistant turns that voice into text, finds the best answer on the web, and then reads it aloud. Voice search optimization helps your content become that answer by making it clear, fast, and easy for search engines to understand.
When users ask voice assistants like Google Assistant, Alexa, or Siri a question, they usually phrase it as a conversation:
- “What’s the best pizza place near me?”
- “How do I improve my website’s SEO?”
These searches are longer, more natural, and often include local intent.
Voice search optimization involves:
- Using conversational keywords and natural language.
- Writing content that answers specific questions directly.
- Adding structured data (schema markup) so search engines can understand your content better.
- Improving website speed and mobile responsiveness, because most voice searches happen on mobile devices.
- Strengthening local SEO, since many voice queries include “near me” or location-based terms.
The goal is simple: make your website the answer that voice assistants read aloud.
Also read: Top 10 AI SEO Tools to Use in 2026
How Voice Search Optimization Works
Voice search optimization focuses on making your website content easy for voice assistants such as Google Assistant, Siri, Alexa, and AI search engines to understand and deliver as spoken answers. It’s not just about ranking higher—it’s about being the one result that gets read aloud.
The Voice Search Process
Wake word and recording
- Your device listens for a wake word like “Hey Google” or “Alexa”.
- After detecting it, the microphone records what you say and sends the audio securely to the assistant’s servers.
Speech‑to‑text (automatic speech recognition)
- Advanced speech recognition systems turn your voice into text.
- In 2026 these systems handle different accents, background noise, mixed languages, and natural speed much better than before, thanks to large AI models.
Understanding the meaning (NLP and intent)
- Natural Language Processing (NLP) looks at the text to figure out what you really want: information, a nearby place, a product, a reminder, or an action.
- The system breaks your sentence into entities (like “voice search”, “2026”), context (“how does it work”), and intent (you want an explanation, not a purchase).
Matching your intent with results
- For informational questions, the assistant queries a search engine and checks sources like web pages, featured snippets, knowledge panels, and local listings.
- For local or “near me” queries, it leans on map data, business profiles, reviews, and GEO signals to find the best nearby options.
Ranking and selecting an answer
- The ranking system evaluates many factors: relevance, page quality, page speed, mobile friendliness, local proximity, and whether the content gives a clear, direct answer.
- In many cases the assistant prefers results that already appear as featured snippets, FAQ rich results, or local pack entries, because these are easy to read aloud.
Generating and speaking the response
- Once a result is chosen, the assistant formats the answer. Sometimes it reads a short extract from a web page; other times it uses information from structured data, business listings, or knowledge graphs.
- Modern assistants can also combine multiple sources and use generative AI to make the answer more conversational, while still grounding it in trusted data.
Learning from behaviour and context
- If you continue the conversation (“And how can I optimize my site for that?”), the assistant remembers the context instead of starting from zero.
- Over time, it personalizes results based on your language, location, device, history, and preferences, which is why two people can get slightly different spoken answers to the same question.
In simple terms, voice search is a chain: voice → text → meaning → best result → spoken answer, powered at each step by AI, NLP, and classic search ranking signals. Websites that are fast, mobile‑friendly, locally optimized, and written in natural, question‑based language are the ones most likely to be chosen as that spoken answer.
Also read: Is SEO a Good Career?
Voice search vs traditional text SEO
How to write content that works for both
To make your “voice search vs traditional text SEO” section perform well and still sound human:
- Start with a clear, one‑paragraph explanation that compares the two in simple terms.
- Use subheadings like “How people search”, “What changes for SEO”, and “Why you need both” for clean structure.
- Write short sentences and avoid repeating the same keyword; use natural variations like “voice search”, “spoken queries”, “typed search”, “text‑based search” etc.
- Add a small FAQ or bullet list that answers questions such as “Is voice search replacing text search?” or “Do I need a separate strategy for voice SEO?”.
You can also interlink this section to your main voice search guide on Search Engine Intellect using a contextual anchor like “complete voice search optimization guide”, so users who want more detail can move deeper into your funnel.
Why Voice Search Optimization Matters
Voice search optimization matters because it connects your content to the way people actually speak, not just how they type. As more searches happen through phones, smart speakers and AI assistants, businesses that ignore voice behavior lose visibility, traffic and leads to competitors who are optimized for natural, spoken queries.
Here’s why it matters:

1. Massive Growth in Voice Searches
- Over 58% of internet users use voice search daily.
- Smart speaker sales have crossed 500 million devices globally, making voice queries more accessible than ever.
2. Higher Conversion Rates
- Voice searches are 30% more likely to lead to a purchase compared to typed searches because users often have higher intent.
- Local voice searches, like “best dentist near me”, have a 50% higher chance of resulting in a store visit within 24 hours.
3. Impact on Local Businesses
- Nearly 76% of smart speaker users search for local information weekly.
- Businesses optimized for voice search see an average 20–30% increase in foot traffic from “near me” searches.
4. Featured Snippets Dominate Voice Results
- Over 60% of voice search answers come from featured snippets, making structured and clear content critical for ranking.
5. Mobile-First & Hands-Free Future
With more people multitasking—driving, cooking, or working—voice search offers the fastest, most convenient option.
72% of voice searches happen on mobile devices, aligning with the mobile-first indexing era.
Voice Search by the Numbers—At a Glance
| Insight | Stat |
|---|---|
| Global adoption | 20.5% of users |
| Devices in use | 8.4 billion voice assistants |
| U.S. voice users | 153.5 million , rising to 162.7 million (2027) |
| Mobile voice search | 27% of users |
| Local intent voice queries | 76% “near me” |
| Voice shopping | 49% of U.S. consumers, $81.8B market |
| Smart speaker ownership | 75% of households |
| Market value | $6.4B (2023) to $110B (2033) |
| Local searches via voice | 58% of consumers use voice for local info |
Ranking factors in Voice Search Optimization
Key ranking factors in voice search optimization centre on three big pillars: strong technical performance, clear and helpful content, and local plus structured signals that make it easy for assistants to read and trust your answers.
When these elements work together, your pages are more likely to be picked as the spoken result on devices like smartphones, smart speakers, and in‑car systems.
1. Website speed and mobile experience
Search engines prefer pages that load fast and work smoothly on mobile because most voice searches happen on phones. Slow, cluttered pages increase bounce rate and reduce the chance that your answer will be selected over a cleaner, faster competitor.
Key points:
- Use responsive design so content looks good on every screen.
- Compress images, reduce heavy scripts, and fix Core Web Vitals issues like slow load and layout shift.
2. Conversational, question‑based content
Voice queries sound like natural speech: “What is voice search optimization?” or “How can I rank higher in voice search this year?”. Content that mirrors this style performs better because search engines can directly match user questions to your headings and paragraphs.
Best practices:
- Include long‑tail, question‑type keywords (who, what, where, when, why, how) in headings and FAQs.
- Write in simple, conversational language so an assistant can read it aloud without sounding robotic.
3. Featured snippets and clear answer blocks
Many voice results are pulled from featured snippets or “position zero” answers. If your page already owns the snippet, your chances of being read out by the assistant increase sharply.
To support this:
- Start sections with a short, direct definition or answer (around 40–50 words).
- Use bullet lists and tables to explain steps, pros and cons, or comparisons in a clean format that is easy to extract.
4. Local SEO and “near me” signals
A large share of voice searches carry local intent, such as “near me”, “open now”, or “[service] in [city]”. For institutes, agencies, clinics, and other local businesses, this is one of the strongest ranking factors in voice search.
Important actions:
- Optimize your Google Business Profile with correct name, address, phone, hours, categories, and services.
- Use local keywords and FAQs on city or area‑specific pages, and keep NAP details consistent across directories.
5. Schema markup and structured data
Schema markup gives search engines extra context about your content, which helps them understand and surface it for voice queries. It is especially powerful for FAQs, local businesses, services, and how‑to guides.
High‑impact schema types:
- FAQPage and QAPage for question‑and‑answer content.
- LocalBusiness, Organization, and Service for local visibility and business details like reviews and opening hours.
6. Content relevance, authority and trust
Voice assistants are careful about which sources they quote, so authority and trust matter. Sites with in‑depth, up‑to‑date content, good internal linking, and natural backlinks are more likely to be chosen as the spoken answer.
Focus on:
- Covering topics in depth with supporting sub‑topics, examples, and FAQs.
- Showing expertise (author bios, case studies, transparent contact info) and avoiding thin or duplicated content that might trigger spam systems.
7. Natural language and user intent alignment
Finally, ranking in voice search depends on how well your page satisfies the real intent behind a question, not just exact keywords. Content that anticipates follow‑up questions and guides users smoothly through their journey tends to perform better across both voice and classic search.
To align with intent:
- Map each key question to a clear answer and a helpful next step, such as a deeper guide or service page.
- Avoid over‑optimizing with repeated phrases; instead, answer naturally and let related terms appear where they make sense.
Also read: Email Marketing Course in Bareilly – Lead Generation Training
How to Optimize for Voice Search
Optimizing for voice search requires a strategic approach that addresses the unique characteristics of spoken queries. Here’s a comprehensive guide to implementing effective voice search optimization in 2026.
1. Switch to conversational, question‑based keywords
Voice search queries are conversational and often longer than text-based searches. To optimize effectively:
Use Natural Speech Patterns:
- Write content that mimics how people actually speak
- Focus on long-tail keywords that match natural speech patterns
- Target full-sentence questions that voice searchers will likely ask
Example Keyword Transformations:
| Traditional Keywords | Voice Search Keywords |
|---|---|
| “pizza delivery” | “Where can I order pizza for delivery near me tonight?” |
| “SEO services” | “What are the best affordable SEO services for small businesses?” |
| “weather forecast” | “What’s the weather going to be like tomorrow morning?” |
Implementation Strategy:
- Use phrases that answer specific questions, like “What’s the best pizza place near me?”
- Incorporate these keywords into your content and meta descriptions
- Balance priorities across both short-tail and long-tail keywords
2. Optimize for Featured Snippets
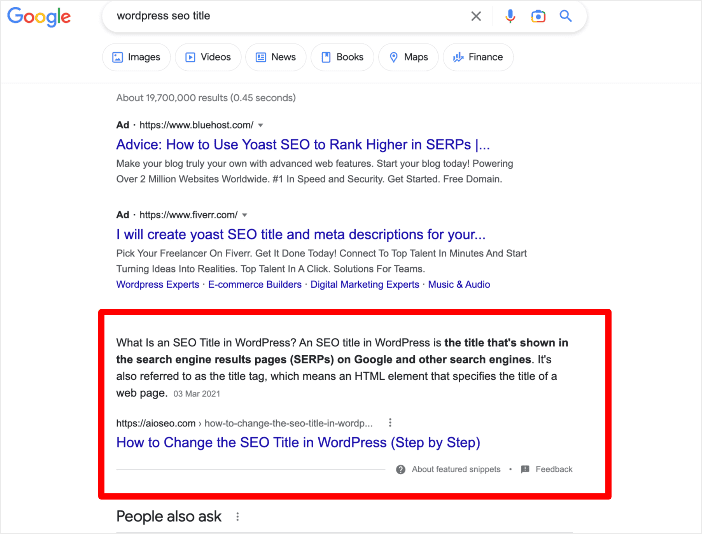
Many voice answers are taken directly from featured snippets, definition boxes, and list snippets. To target these:
- Use clear definitions in the first 40–50 words of a section
- Format step processes as numbered lists and benefits as bullets
- Include comparison tables where helpful, using short and readable cells
For example, a neat comparison between text and voice SEO (see table below) can increase your chance of getting a snippet for “voice search vs traditional search”.
Text vs voice SEO focus (example table)
3. Create AEO‑ready FAQ and answer blocks
Answer Engine Optimization (AEO) focuses on structuring content so that search engines can extract precise answers for specific questions. The easiest way to do this is:
- Add FAQ sections with direct one‑paragraph answers
- Use FAQPage schema to help assistants identify questions and responses
- Keep answers concise but helpful so they can be read aloud easily
You can also create dedicated “What is voice search optimization?” or “How to do SEO for voice search: 9 tips” articles and interlink them from your main guide to build depth. This structure helps both classic SEO and emerging answer engines.
4. Prioritize Local SEO Optimization
A big share of voice searches have local intent such as “near me”, “open now”, or “best in [city]”. To capture this:
Also read: Gemini vs. ChatGPT: Which is Better AI Tool in 2026?
Local Optimization Checklist:
Google Business Profile:
- Claim your Google My Business profile and keep it updated
- Add accurate contact details, business hours, and location information
- Upload high-quality photos and maintain current business information
Local Content Strategy:
- Include local keywords to enhance visibility in “near me” searches
- Use AdWords location extensions to show up in “near me” searches
- Publish location-specific content to increase relevance to local searches
You can also create GEO‑specific landing pages for key service areas with embedded maps, local testimonials, and FAQs like “How to find a digital marketing agency in Bareilly with voice search?”. Structured LocalBusiness data and review schema further improve eligibility for voice results.
5. Use schema markup for rich results and entities
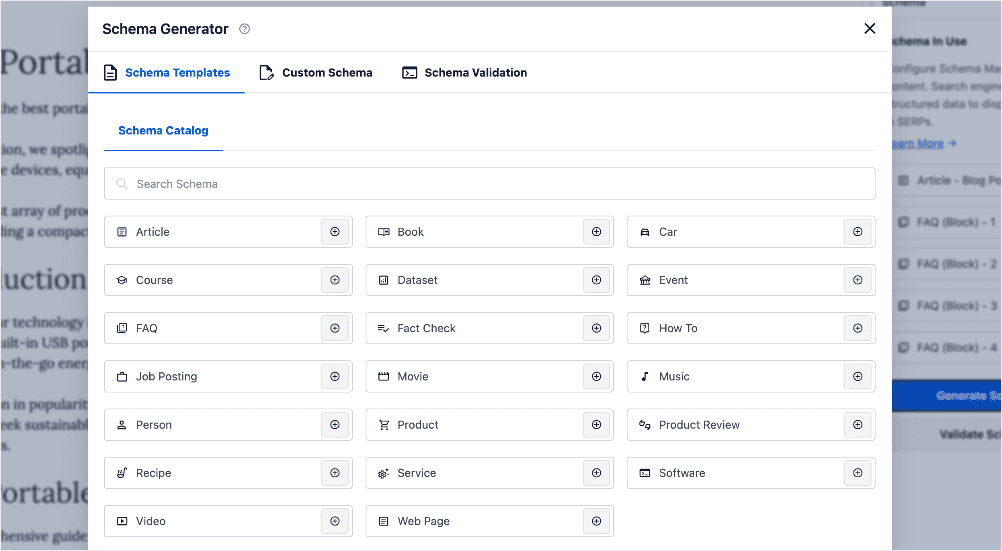
Schema helps search engines understand context: whether something is a product, course, how‑to, local service, or FAQ. For voice search optimization, high‑impact schemas include:
Essential Schema Types:
| Schema Type | Purpose | Voice Search Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| FAQ Schema | Question-based content | Direct answer extraction |
| Local Business Schema | Location information | “Near me” query optimization |
| Review Schema | Product/service ratings | Trust signals for recommendations |
| How-to Schema | Step-by-step instructions | Process-based queries |
Proper schema also feeds into knowledge graphs, which power many direct answers in assistants and smart displays.
6. Improve page speed, mobile UX and CWV
Voice searches are often conducted on mobile devices, making technical optimization essential.
Technical Requirements:
Mobile-First Design:
- Ensure responsive design across all screen sizes
- Optimize page loading speed for mobile devices
- Get the technical details right including page loading speed, mobile compatibility, and HTTPS security
Performance Optimization:
- Improve page speed as voice searches prioritize fast-loading sites
- Implement Core Web Vitals compliance
- Use Content Delivery Networks (CDN) for faster content delivery
7. Create Question-Based Content
Voice searches often take the form of questions. Structure your content to answer these naturally.
Content Strategy:
Question Types to Target:
- What questions: Define concepts and provide explanations
- How questions: Offer step-by-step instructions
- Where questions: Include location-specific information
- When questions: Address timing and scheduling concerns
- Why questions: Explain benefits and reasoning
Content Format:
- Make content easy to read, conversational, and in line with your brand’s voice
- Use clear headings and subheadings for better content organization
- Provide direct, concise answers to common queries
8. Focus on User Intent Understanding
Start by grasping what users are looking for when they use voice search. Many voice queries are location-specific or seek specific information.
Intent Analysis:
Local Intent:
- Claim and update your Google My Business listing to boost visibility on Google Maps
- Target location-based queries and “near me” searches
- Include geographic context in content
Informational Intent:
- Create comprehensive content that addresses user questions
- Provide immediate, specific answers
- Focus on problem-solving content
9. Monitor voice search tracking and reports
Classic analytics show overall organic performance, but voice search tracking focuses on queries, devices, SERP features, and impressions associated with voice behavior. You can:
Key Performance Indicators:
| Metric | Measurement Method | Voice Search Relevance |
|---|---|---|
| Featured Snippet Appearances | Google Search Console | Voice assistant answer source |
| Mobile Traffic Increase | Google Analytics | Voice search device preference |
| Local Pack Rankings | Local rank tracking tools | “Near me” search visibility |
| Conversational Keyword Rankings | SEO monitoring platforms | Long-tail voice query performance |
Implementation Timeline
Immediate Actions (Week 1-2):
- Audit current content for conversational keyword opportunities
- Optimize Google Business Profile with complete information
- Create initial FAQ pages addressing common questions
Short-term Goals (Month 1-3):
- Implement structured data markup across key pages
- Develop question-based content strategy
- Optimize for featured snippets on target keywords
Long-term Strategy (3-6 Months):
- Build comprehensive local SEO presence
- Create extensive question-and-answer content library
- Monitor performance and refine optimization strategies
Voice search optimization requires a holistic approach that combines technical excellence with natural, conversational content creation. By focusing on long-tail keywords, optimizing for featured snippets, and prioritizing local SEO, businesses can effectively capture the growing voice search market while providing valuable user experiences across all search modalities.
Also read: Google Ads Training in Bareilly – PPC Mastery Course
Advanced voice SEO formulas
Short formulas to prioritize opportunities
To make decisions, you can convert qualitative insight into simple formulas. For example, a Voice Opportunity Score (VOS) can be defined as:VOS=Average positionImpressions for question keywords×CTR
Queries with many impressions, low position, and moderate CTR give strong upside when optimized for featured snippets and FAQs. Focus your efforts on these first, building tighter answer blocks and adding FAQ schema for them.
Another idea is a Snippet Readiness Index (SRI):SRI=Content clarity factor+Schema coverage factor+Page speed factor
Each component can be scored from 1 to 3 based on clarity of the main answer, correct schema usage, and performance scores so teams can rank pages and fix the weakest ones.
Combining CTR, position and SERP features
Voice assistants lean towards pages that already win snippets or top three organic positions. In your voice search ranking report, add columns for:
- Query and intent type
- Current position and CTR
- Presence of snippet, FAQ rich result, local pack, or knowledge panel
- Actions taken and next steps
This structured view makes it easier to decide where to apply advanced voice SEO formulas, which pages deserve full rewrites, and which can be improved with small, targeted tweaks like better intros or shorter answer boxes.
Also read: Top 10 Digital Marketing Institutes in Bareilly
The Future of Voice Search
Voice search is not just a trend—it’s shaping the future of how users interact with the internet. As technology advances, its role in SEO and digital marketing will only grow stronger.
1. Integration with AI and Generative Search
- AI-powered assistants like Google Assistant, Alexa, and Siri are getting smarter.
- With generative AI in search (like Google’s Search Generative Experience), answers will become more conversational, detailed, and context-aware.
- Future SEO will focus on content that mimics natural human conversation.
2. Multimodal Search Will Rise
- Users won’t rely only on voice—they’ll use a mix of voice, text, and image-based queries.
- Voice search will often be the first step in a multi-step search journey.
- Brands will need to optimize for cross-device and multimodal experiences.
3. Stronger Focus on Local and Hyperlocal Search
- Voice search will become the primary way people find nearby businesses.
- Expect “near me” and “open now” queries to continue dominating voice search results.
- Businesses without a complete Google Business Profile will miss out.
4. Voice Commerce (V-Commerce) Will Explode
- By 2030, voice commerce may contribute up to 30% of global e-commerce revenue.
- Smart speakers and in-car voice systems will play a huge role in shopping decisions.
- Brands must prepare with voice-friendly product descriptions and purchasing flows.
5. Personalized and Predictive Voice Search
- Voice assistants will predict user needs based on habits, location, and preferences.
- This means your content must be contextually rich and deeply aligned with user intent.
6. Hands-Free SEO Becomes the Norm
- From cars to smart kitchens, users are searching without touching a screen.
- Voice search SEO will become a key part of wearables, IoT, and automotive search experiences.





